Test run of all scanners¶
The following is a complete script to test-run all the scanning algorithms wrapped by pyScannerBit. It can be found in the git repo at tests/test_all_scanners.py. NOTE: external scanners are current non-functional so they are left out of this test:
"""Demo script which runs all the (serious) scanners to which pyScannerBit has access"""
import numpy as np
import math
import pyscannerbit.scan as sb
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpi4py import MPI
rank = MPI.COMM_WORLD.Get_rank()
size = MPI.COMM_WORLD.Get_size()
# Regenerate scan data?
new_scans = True
# Test function
def rastrigin(scan,x,y,z):
X = [x,y,z]
A = 10
return - (A + sum([(x**2 - A * np.cos(2 * math.pi * x)) for x in X]))
# Prior transformation from unit hypercube
def prior(vec, map):
map["x"] = -4 + 8*vec[0] # flat prior over [-4,4]
map["y"] = -4 + 8*vec[1]
map["z"] = -4 + 8*vec[2]
# Settings for quick and dirty scans. Won't do very well, because the test function is
# actually rather tough!
# Don't have to specify all scanner options; anything missing will revert to defaults (see defaults.py)
scanner_options = {}
scanner_options["multinest"] = {"tol": 0.5, "nlive": 100}
scanner_options["polychord"] = {"tol": 1.0, "nlive": 20}
scanner_options["diver"] = {"convthresh": 1e-2, "NP": 300}
scanner_options["twalk"] = {"sqrtR": 1.05}
scanner_options["random"] = {"point_number": 10000}
scanner_options["toy_mcmc"] = {"point_number": 10} # Acceptance ratio is really bad with this scanner, so don't ask for much
scanner_options["badass" ] = {"points": 1000, "jumps": 10}
scanner_options["pso"] = {"NP": 400}
scanners = ["twalk","badass","pso"]
colors = ["r","b","g"]
if size is 1:
scanners += ["random","toy_mcmc"] # "random" and "toy_mcmc" are not MPI compatible.
colors += ["c","y"]
Nscans = len(scanners)
results = {}
# Do all scans
for s in scanners:
# Create scan manager object
myscan = sb.Scan(rastrigin, prior_func=prior, scanner=s, scanner_options=scanner_options[s])
if new_scans:
print("Running scan with {}".format(s))
myscan.scan()
else:
print("Retrieving results from previous {} scan".format(s))
results[s] = myscan.get_hdf5()
# Plot results
# Only want to do this on one process
if rank is 0:
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(4*Nscans,8))
for i,(s,c) in enumerate(zip(scanners,colors)):
x,y = results[s].get_params(["x","y"])
ax = fig.add_subplot(2,Nscans,i+1)
ax.set_title("{0} (N={1})".format(s,len(x)))
ax.scatter(x,y,c=c,label=s,s=0.5)
ax = fig.add_subplot(2,Nscans,i+1+Nscans)
results[s].plot_profile_likelihood(ax,"x","y")
ax.legend(loc=1, frameon=True, framealpha=1, prop={'size':10})
plt.tight_layout()
fig.savefig("test_all_scanners.png")
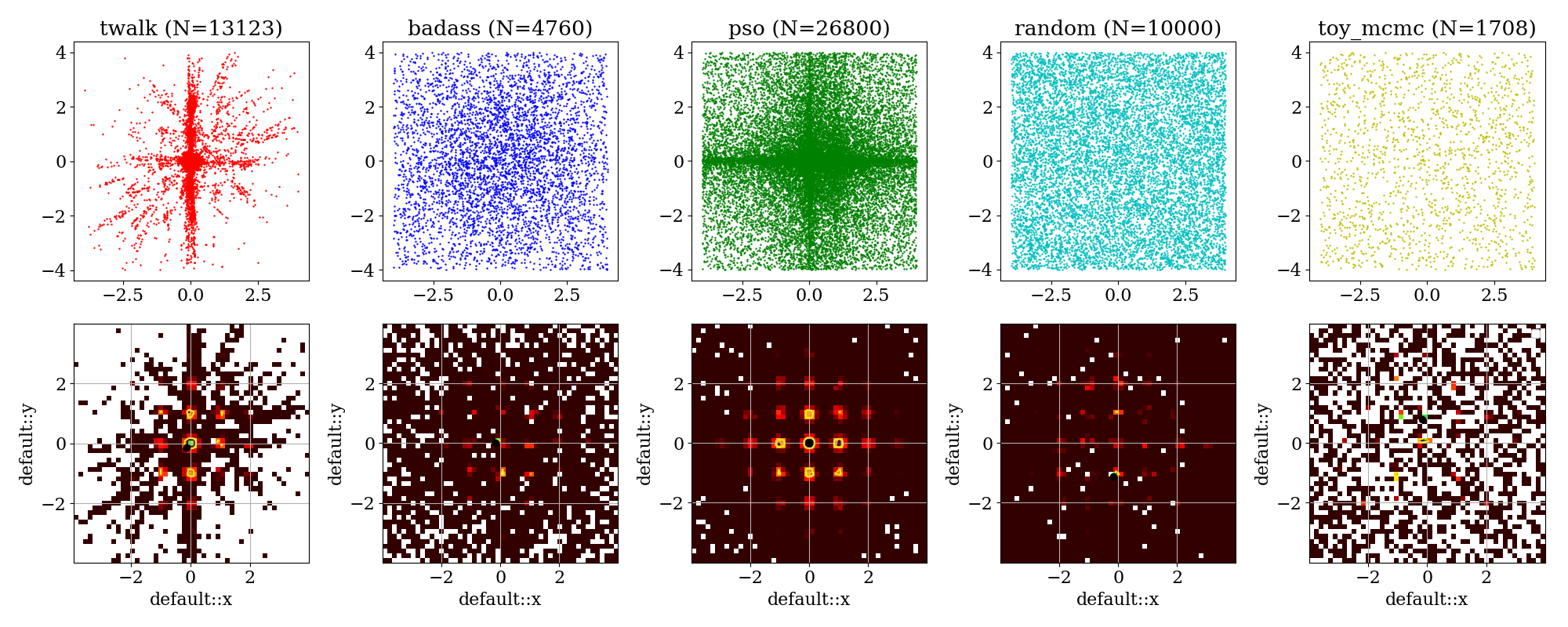
Profile likelihood and scatter plots of rastrigin test function, scanned quickly by all available algorithms¶